
KPI: Key Performance Indicator
The purpose is to check the performance of Network. We have categories of KPI and numbers of KPI of each category. In the Optimization process we have to check the KPI value to monitor and optimize the radio network performance in order to provide better subscriber quality or to achieve better use of installed network resources . Typically KPI can be categorized into following subcategories:
|
Let's break down KPI per each category:
📈 Accessibility KPI
Are used to measure properly of whether services requested by users can be accessed in given condition, also refers to the quality of being available when users needed. eg. user request to access the network, access the voice call, data call, ......
📈 Retainability KPI
Are used to measure how the network keep user's possession or able to hold and provide the services for the users
📈 Mobility KPI
Are used to measure the performance of network which can handle the movement of users and still retain the service for the user, such as handover,...
📈 Integrity KPI
Are used to measure the character or honesty of network to its user, such as what is the throughput, latency which users were served.
📈 Availability KPI
Are used to measure the availability of network, suitable or ready for users to use services.
📈 Utilization KPI
Are used to measure the utilization of network, whether the network capacity is reached its resource.
KPIs for LTE RAN (Radio Access Network)
| LTE KPI | INDICATORS |
|
Accessibility KPI
|
Are used to measure properly of whether services requested by users can be accessed in given condition, also refers to the quality of being available when users needed. eg. user request to access the network, access the voice call, data call, ......
|
|
Retainability KPI
|
Are used to measure how the network keep user's possession or able to hold and provide the services for the users
|
|
Mobility
KPI |
Are used to measure the performance of network which can handle the movement of users and still retain the service for the user, such as handover,...
|
|
Integrity
KPI |
Are used to measure the character or honesty of network to its user, such as what is the throughput, latency which users were served.
|
|
Availability
KPI |
Are used to measure how the network keep user's possession or able to hold and provide the services for the users
|
|
Utilization
KPI |
Are used to measure the utilization of network, whether the network capacity is reached its resource.
|
ACCESSIBILITY KPI:
☰ RRC Setup Success Rate
RRC setup success rate is calculated based on the counter at the eNodeB when the eNodeB received the RRC connection request from UE. Number of RRC connection attempt is collected by the eNodeB to the measurement at point A, and the number of successful RRC connection calculated at point C. Here's an illustration:


☰ ERAB setup success rate
ERAB setup success rate KPI shows the probability of success ERAB to access all services including VoIP in a cell or radio network. KPI is calculated based counter ERAB connection setup attempt (point A) and successful ERAB setup (point B). The explanation is as given in the following illustration:


☰ Call Setup Success Rate
Call Setup Success Rate KPI call setup indicates the probability of success for all service on the cell or radio network. KPI is calculated by multiplying the RRC setup success rate KPI, S1 signaling connection success rate KPI, and ERAB success rate KPI. The table below describes the definition Call Setup Success Rate:

RETAIN-ABILITY KPI:
☰ Call Drop
VoIP call drop arise when VoIP ERAB release is not normal. Each ERAB associated with QoS information.
Here's an illustration of two procedures being done to release ERAB namely: ERAB release indication and the UE context release request:


MOBILITY KPI:
☰
Intra-Frequency Handover Out Success Rate
Intra-Frequency Handover Success Rate Our KPI shows intra-frequency handover success rate of locall cell or radio network to the intra-frequency neighboring cell or radio network. Intra-frequency HO included in a single cell eNodeB or different eNodeB.
Intra-frequency HO scenario shown in the figure below:
Intra-frequency HO scenario shown in the figure below:

No attempt HO calculations at point B. When ENodeB sending RRC connection reconfiguration message to the EU, he will do the handover. ENodeB will count the number of times the HO attempt at the source cell. HO calculation of success is at point C. The HO ENodeB count the number of the source cell when ENodeB receive RRC connection reconfiguration message complete of the EU.
Here's a scenario intra-frequency handovers inter ENodeB:
Here's a scenario intra-frequency handovers inter ENodeB:

Handover attempt occurs at point B, when the source ENodeB (S-eNodeB) sends RRC connection reconfiguration message to the UE. He decided to conduct inter ENodeB HO. in this KPI, the source and the target cell work on the same frequency. The number of the attempt HO calculated at the source cell.
The number of successful HO occurs at point C. During HO, HO amount which success is measured in the cell souce. This measurement appears typing S-eNodeB received a UE context release message from the target eNode B (T-eNodeB), or the UE context release command from the MME, which shows that the UE-eNodeB T has successfully attach at the T-eNodeB.
The following scenarios illustrate intra frequency B HO - inter ENodeB:
The following scenarios illustrate intra frequency B HO - inter ENodeB:

Following the definition of Intra Frequency Out Handover Success Rate KPI:

☰ Inter-RAT Handover Out Success Rate (LTE to WCDMA)
Inter RAT Handover Out Success rate shows the success rate KPI HO from LTE cell or radio network to a WCDMA cell.
Here's a scenario out inter RAT handover success rate:
Here's a scenario out inter RAT handover success rate:

Inter RAT handover success rate out

INTEGRITY KPI:
☰ E-UTRAN IP Throughput
A KPI that shows how E-UTRAN impacts the service quality provided to an end-user.
Payload data volume on IP level per elapsed time unit on the Uu interface. IP Throughput for a single QCI:
Payload data volume on IP level per elapsed time unit on the Uu interface. IP Throughput for a single QCI:
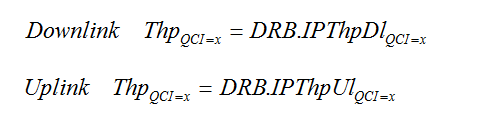

To achieve a throughput measurement that is independent of bursty traffic pattern, it is important to make sure that idle gaps between incoming data is not included in the measurements. That shall be done as considering each burst of data as one sample.
ThpVolDl is the volume on IP level and the ThpTimeDl is the time elapsed on Uu for transmission of the volume included in ThpVolDl.

☰ E-UTRAN IP Latency
A measurement that shows how E-UTRAN impacts on the delay experienced by an end-user.
Time from reception of IP packet to transmission of first packet over the Uu.
To achieve a delay measurement that is independent of IP data block size only the first packet sent to Uu is measured.
To find the delay for a certain packet size the IP Throughput measure can be used together with IP Latency (after the first block on the Uu, the remaining time of the packet can be calculated with the IP Throughput measure).
Time from reception of IP packet to transmission of first packet over the Uu.
To achieve a delay measurement that is independent of IP data block size only the first packet sent to Uu is measured.
To find the delay for a certain packet size the IP Throughput measure can be used together with IP Latency (after the first block on the Uu, the remaining time of the packet can be calculated with the IP Throughput measure).

T_Lat is defined as the time between receiption of IP packet and the time when the eNodeB transmits the first block to Uu.
Since services can be mapped towards different kind of E-RABs, the Latency measure shall be available per QoS group.
Since services can be mapped towards different kind of E-RABs, the Latency measure shall be available per QoS group.
AVAILABILITY KPI:
☰ E-UTRAN Cell Availability
E-UTRAN Cell Availability.
A KPI that shows Availability of E-UTRAN Cell.
Percentage of time that the cell is considered available.
A KPI that shows Availability of E-UTRAN Cell.
Percentage of time that the cell is considered available.

As for defining the cell as available, it shall be considered available when the eNodeB can provide E-RAB service in the cell.
UTILIZATION KPI:
☰ Mean Active Dedicated EPS Bearer Utilization
This KPI describes the ratio of the mean number of active dedicated EPS bearer to the maximum number of active dedicated EPS bearers provided by EPC network, and it is used to evaluate utilization performance of EPC network.
This KPI is obtained by the mean number of dedicated EPS bearers in active mode divided by the system capacity.
This KPI is obtained by the mean number of dedicated EPS bearers in active mode divided by the system capacity.
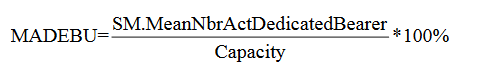
The mean number of simultaneous online and answered sessions together with maximum number of sessions provided by network can reflect system resource utilization. If the value of this KPI is very high, it indicates system capacity is not enough, and needs to be increased.
This KPI is focusing on network view.

